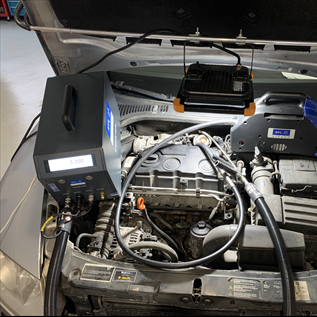
The legally required "Emissions Testing" at the MOT stations is only about 10% of what the emissions test equipment can provide. While there are many drawbacks to measuring with an outdated smoke meter, if used at the tailpipe, it can do a perfect job of measuring the raw emissions of diesel vehicles equipped with DPF filters.
We can use the exhaust gas analysers originally designed for spark-ignition engines only, enhanced with a sensor to measure the nitrogen oxide (NO) component, to diagnose mixture richness and exhaust gas recirculation efficiency on diesel engines.
The method of measuring opacity by "free acceleration" is very questionable. Firstly, it comes from the early diesel era, and then it's a very ineffective alternative for old engines only, but not for complete vehicles. Why?
By measuring the opacity on the intake hose to the differential pressure sensor in front of the DPF filter, we achieve relatively accurate and, above all, repeatable values. Based on this, we can determine without disassembling parts whether the higher degree of particulate filter saturation is occurring because the engine is generating high raw engine smoke.
Analyzátor výfukových plynů hlídá celkem 5 parametrů:
Zatímco u dieselů se diagnostika plynů soustředí kromě čísla Lambda na dvě složky (NO a O2), u zážehových motorů jsou to plyny všechny.
Analyzátor výfukových plynů lze používat i pro kontinuální měření plynů na koncovce výfuku za pomoci chladiče plynů a odlučovače kondenzátu.
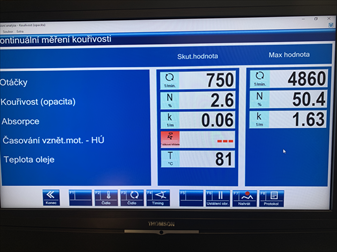
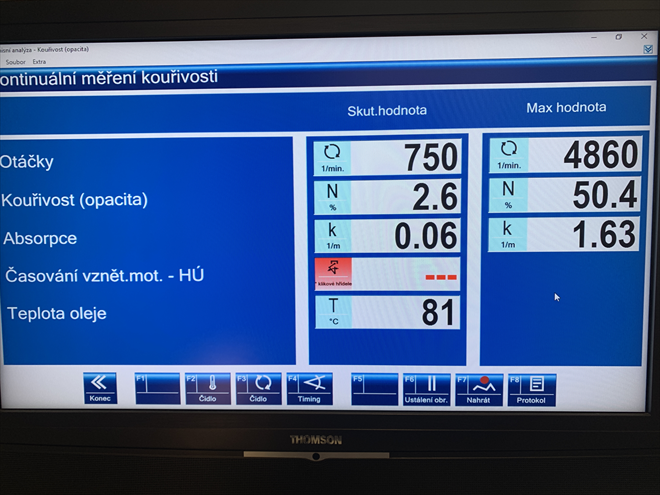
If the engine (raw emissions before DPF) smokes more than approx. 1.3 [1/m], the DPF is overloaded, and its regeneration cycles will be shorter. Engines should produce readings of approximately 0.7 [1/m] to prevent the DPF from clogging frequently and prematurely. Here the smoke meter is a useful diagnostic tool.

While the smoke meter on modern engines measures the "raw" opacity (before the DPF), the particle counter is used to measure at the exhaust tail pipe.

High levels of unburned hydrocarbons at idle will reveal incorrectly atomising injectors.
Komentáře (0)
Vložit soubor